Forest Resources in Jiangsu Province
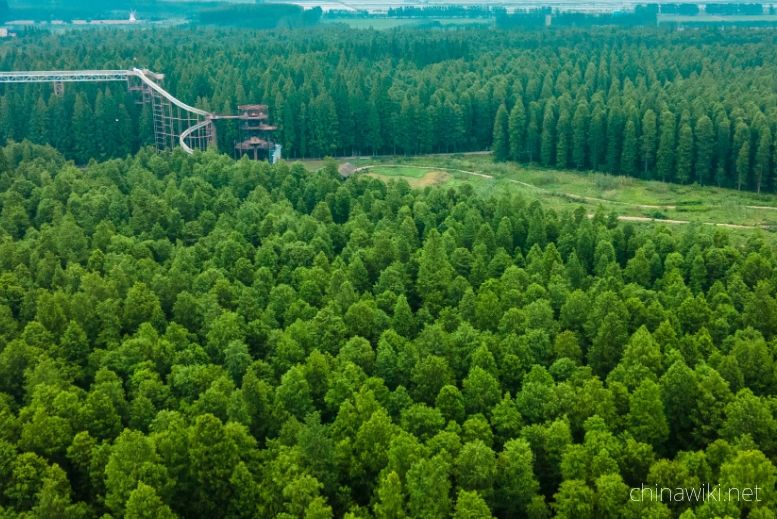
In 2017, the forest area in jiangsu Province was 1.56 million hectares, with a forest coverage rate of 22.9% and a total standing timber volume of 96.09 million cubic meters. There are 6 national forest cities (Wuxi, Yangzhou, Xuzhou, Nanjing, Zhenjiang, Changzhou), 5 national greening model cities (Nanjing, Suzhou, Suqian, Yancheng, Lianyungang), 42 national greening model counties (cities, districts), 53 national greening model units, and 31 national ecological and cultural villages in the province; There are 69 forest parks at or above the provincial level (including 2 specialized parks and 2 ecological parks), including 25 national forest parks and 44 provincial forest parks
On May 7, 2024, the official website of the People's Government of jiangsu Province announced that the forest area in jiangsu Province was 23.4 million mu, with a forest coverage rate of 15.2% and a forest coverage rate of 24.09%. We have built a total of 9 national forest cities, 7 national greening model cities, and 39 national greening model counties (cities, districts)

Forest Resources in Jiangsu Province
-
Jiangsu Province in the Pre Qin Period
Archaeological discoveries indicate that humans existed on the land of Jiangsu as early as the Paleolithic era, and cultural sites from the New Era have also been discovered in various parts of Jiangsu. During the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties, the Jiang
Views: 14 Time 2024-12-28 -
Jiangsu Province during the Ming and Qing Dynasties
In 1368, Zhu Yuanzhang established a political power in Yingtian (now Nanjing) as the capital city. Later, Yingtian changed its name to Nanjing and then to Jingshi, also known as Zhili. After Ming Chengzu established the name Yongle, he moved the capital
Views: 19 Time 2024-12-28 -
Jiangsu Province after the establishment of the People's Republic of China
In June 1949, the entire Jiangsu province was liberated. The territory is divided into three provincial-level administrative regions: northern Jiangsu, southern Jiangsu Administrative District, and Nanjing City. In January 1953, three provincial-level adm
Views: 9 Time 2024-12-28 -
Location and territory of Jiangsu Province
Jiangsu Province is located in the middle of the eastern coastal area of Chinese Mainland, at the lower reaches of the Yangtze River and Huaihe River, bordering the Yellow Sea to the east, Shandong to the north, Anhui to the west, and Shanghai and Zhejian
Views: 13 Time 2024-12-28 -
Climate situation in Jiangsu Province
Jiangsu belongs to a transitional climate from temperate to subtropical, with the Huai River and the main irrigation canal in northern Jiangsu as the boundary. To the north, it belongs to a warm temperate humid and semi humid monsoon climate, while to the
Views: 18 Time 2024-12-28 -
Geological conditions of Jiangsu Province
Jiangsu Province is located in the North China plate, the eastern section of the Qinling Dabie orogenic belt, and the Yangtze plate, which cross the Chinese Mainland. The regional geological background and tectono magmatic activity are obviously different
Views: 11 Time 2024-12-28 -
Hydrological and Water Conservancy Situation in Jiangsu Province
Jiangsu Province spans across rivers and coasts, with numerous lakes and a dense water network, adjacent to land and sea. It is the only province in China with large rivers, lakes, and seas. The Yangtze River spans 433 kilometers from east to west, and th
Views: 260 Time 2024-12-28 -
Water Resources Situation in Jiangsu Province
Jiangsu has abundant water resources, with annual runoff depth ranging from 150-400 millimeters during rainfall. Deep Quaternary loose deposits are widely distributed in the plain areas of Jiangsu Province, with abundant groundwater sources. The total
Views: 104 Time 2024-12-29 -
Land Resources in Jiangsu Province
In December 2021, the main data bulletin of the third national land survey in Jiangsu Province showed that there were 61.4839 million mu of arable land in the province, including 42.5758 million mu of paddy fields, accounting for 69.25%; 11.2311 million a
Views: 131 Time 2024-12-29 -
Forest Resources in Jiangsu Province
In 2017, the forest area in Jiangsu Province was 1.56 million hectares, with a forest coverage rate of 22.9% and a total standing timber volume of 96.09 million cubic meters. There are 6 national forest cities (Wuxi, Yangzhou, Xuzhou, Nanjing, Zhenjiang,
Views: 105 Time 2024-12-29 -
Port resource situation in Jiangsu
As of the end of 2021, Jiangsu Province had 5909 productive port berths and 529 berths of over 10000 tons. The comprehensive annual throughput capacity of ports reached 2.38 billion tons, and multiple indicators such as port cargo throughput capacity and
Views: 110 Time 2024-12-29 -
The situation of natural disasters in Jiangsu
Jiangsu Province has a wide range of meteorological disasters and their impact, making it one of the provinces in China where meteorological disasters occur more frequently. The main meteorological disasters include rainstorm, severe convection, flood, th
Views: 108 Time 2024-12-29