Yin Ruins Scenic Area (Yin xu)
Yin Ruins, formerly known as "Northern Mongolia" , is the ruins of the capital city in the late Shang Dynasty of China, located in Anyang City, Henan Province. In Pan Geng's fourteenth year, Pan Geng, the twentieth monarch of Shang Dynasty, moved his capital to Northern Mongolia (now Anyang, Henan Province) and renamed it "Yin". Pangeng 15 years, began to build Yindu. From Pangeng's moving to Yin Dynasty to Emperor Xin's subjugation in 1046 B.C., Yin has been the political, economic, cultural and military center of the late Shang Dynasty in China. It was ruled by 12 kings of eight generations, including Pangeng, Xiaoxin, Xiaoyi, Wuding, Zugeng, Zujia, Linxin, Kangding, Wuyi, Wending, Diyi and Dixin in 273 years.
At the beginning of the 20th century, Yin Ruins were famous for excavating oracle bone inscriptions. In 1928, the archaeological excavation of Yin Ruins officially began. A large number of capital building sites and abundant cultural relics represented by Oracle Bone Inscriptions and bronzes were unearthed. The brilliant bronze civilization of the late Shang Dynasty in China was systematically displayed, and the science of Yin Shang society as a religion of history was established. Learning status. It was ranked the first of 100 major archaeological discoveries in China in the 20th century.
About 150,000 pieces of inscribed oracle bones have been unearthed in Yin Ruins. The information recorded in oracle bone inscriptions advanced the credible history of Chinese written records to the Shang Dynasty, and a new discipline, oracle bone science, emerged.
Yin Ruins is the first capital city in China that has been proved by Archaeology and oracle bone inscriptions. It consists of Yin Ruins'mausoleum, Yin Ruins' palace and temple sites, and Huanbei Shang City sites.
In March 1961, the State Council listed Yin Ruins as the first batch of key national cultural relics protection units. In July 2006, Yin Ruins was listed on the World Heritage List by UNESCO. It is now a national AAAAA-level tourist attraction. On October 13, 2018, the Ninetieth Anniversary of the Scientific Excavation of Yin Ruins and the Yin Ruins Development and Archaeology Forum were held. On October 11, 2018, it was selected as the "National Practical Education Base for Primary and Secondary School Students".
Yin Ruins is located around Xiaotun Village, Yindu District, Anyang City, Henan Province. Its geographic coordinates are 114 degrees 18'50 E, 36 degrees 07'36 N, with an elevation of about 80 m, a length and width of about 6 km, a total area of 36 square kilometers, a core area of 414 hectares of heritage reserves and a buffer area of 720 hectares.
The overall layout of Yin Ruins is tidy, with the Yin Ruins Palace and Temple Site in Xiaotuncun as the center, distributed in a circular pattern along both sides of the Huanhe River. Existing relics mainly include Yinxu Palace temple site, Yinxu imperial mausoleum site, Huanbei Shangcheng site, Hougang site and settlement site (clan yi), family cemetery group, oracle bone cellar, copper casting site, handicraft workshop, etc.
Cultural relics
Palace temple
Palace Temple site is located in Xiaotun Village and Garden Village on the South Bank of Huanhan River, Anyang City, Henan Province. It is 1000 meters long in North and south, 650 meters wide in East and west, and has a total area of 71.5 hectares. It is the place where Shang King handled government affairs and lived. It is also the most important site and component of Yin Ruins, including more than 80 building bases such as palaces and temples. On the West and south sides of the palace temple site, there is a man-made excavation to defend Haogou, which surrounds the palace temple and plays a similar role as the palace city.
There is also a good Tomb of Wuding's spouse in the palace and temple area. It is the only Tomb of Shang royal family members that has been found so far. It is also the only Tomb of Shang royal family members who can contact oracle bone inscriptions and determine the age, owner and identity of the tomb. There were 16 dead people in the tomb, 1928 unearthed objects, including 468 bronzes, 755 jades and 564 bones, and nearly 7000 seashells.
There are also many oracle bones pits in the palace and temple area of Yinxu, with a total of about 15,000 pieces of oracle bones unearthed.
Wang Ling site
Wang Ling Site is located in the North highland of Houjiazhuang and Wuguancun on the North Bank of Huanhe River, Anyang City, Henan Province. It is about 450 meters long in East and west, 250 meters wide in North and south, and has a total area of 11.3 hectares. Since 1934, there have been 13 large tombs, more than 2,000 accompanying tombs, sacrificial pits and Chema pits. A large number of exquisite bronzes, jades, stone and pottery have been unearthed. They are recognized as the site of the Yin and Shang Kings'Mausoleum in the academic circles. Among them, the Eastern District has a large number of sacrificial pits arranged in an orderly manner. There are many human and animal skeletons in the pits. It is a public sacrificial venue for the Yin royal family to sacrifice ancestors. It is now opened up as the M260 exhibition hall.
In addition, the stepmother Wudafangding unearthed in the east of the imperial mausoleum is the heaviest bronze found so far.
Bei Bei Shang Cheng
Huanbei Mall is located in Huanhuazhuang on the North Bank of Huanhe River in Anyang City, Henan Province. Its site is generally square, 2.15 kilometers wide in East and west, 2.2 kilometers long in North and south, and its total area is about 4.7 square kilometers. There are compacted grooves around the city wall. The discovery of the Shangcheng ruins in Huanbei extends the historical period of the Shang Dynasty and the scope of the Yin Ruins.
The site of Huanbei Shangcheng is earlier than the traditional Yinxu late Shang culture and a little later than Zhengzhou early Shang culture. It is probably a capital site in the middle and late Shang Dynasty.
Xiongnu tombs
On May 3, 2017, it was reported that 18 Hun tombs were discovered by archaeologists during an archaeological excavation in the Yinxu Grand Site Reserve. These Xiongnu tombs are arranged in a neat order and have the same shape. Judging from the unearthed artifacts, these tombs are later than the Yin Ruins period, and differ from the form and content of the Central Plains tombs. Its era should be from the late Eastern Han Dynasty to the Wei and Jin Dynasties, about 1800 years ago.
Architectural features
The buildings of Shang Dynasty represented by palaces, temples and mausoleums are solemn, simple and elegant in shape, reflecting the unique sense of balance, order and aesthetic interest of ancient Chinese architecture, and embodying the palace construction pattern, architectural art, architectural methods and architectural techniques of the Yin and Shang Dynasties, which represent the early period of ancient China. Advanced level of palace architecture. The Huanbei Mall of Yin Ruins, with its large walls, majestic palaces, and especially its strict "central axis" layout, has become a feature of Chinese cities of past dynasties for thousands of years.
Historiography value
The excavation of Yin Ruins almost completely changed the traditional historical outlook of the three generations of Xia, Shang and Zhou dynasties, established the scientific status of Yin and Shang society as a faithful history, established a reliable chronological basis for Shang and Zhou archaeology, played a basic role in tracing back to the early Shang and Xia cultures, and filled in Erligang, Zhengzhou as the representative of Zhongzhong. The gap between Shang culture and late Shang culture represented by Yin Ruins perfected the chronological framework of Shang Dynasty.
The cultural relics of Yin Ruins, represented by bronzes and jade wares, show that the handicraft industry in Yin Ruins period was unprecedentedly developed, not only with complete categories, but also with a high level of craftsmanship. Some major handicraft production sectors, such as bronze casting, jade making, pottery, bone making, car making, textile and so on, have reached a considerable scale. White pottery and primitive pottery in this period occupied an important position in the history of Chinese ceramics. The Shang Dynasty carriages unearthed from Yin Ruins used a large number of bronze components, single set of double wheels, exquisite and complex structure, reflecting superb mechanical, bronze casting and other composite technology.
The burial system, distribution pattern, burial methods and sacrificial rituals of Yinxu Imperial Mausoleums reflect the social organization, class status, hierarchy and kinship in the late Shang Dynasty. They represent the highest level of the construction of ancient Imperial Mausoleums in China and are imitated by the later dynasties, gradually forming a unique Chinese feature. The mausoleum system. Meanwhile, the funeral customs of Yin Ruins, represented by people's sacrifice, people's sacrifice, carriage and horse's sacrifice and animal sacrifice, highlighted the ritual system with hierarchy as the core during the Yin Ruins Period and embodied the funeral customs at that time.
Archaeological influence
1. The excavation of Yin Ruins is a product of the combination of Chinese traditional epigraphy and western field archaeology, and a symbol of the rise of modern Chinese archaeology.
2. The excavation of Yinxu palace area and Wang Ling area and the discovery of a large number of precious cultural relics such as bronzes and jades have attracted the attention of both Chinese and foreign academic circles and established the international status of Chinese archaeology.
3. The discovery of "three layers" in 1931 at Hougang Site in Anyang by Liang Siyong, for the first time, divided the relative chronological relationships among Yangshao Culture, Longshan Culture and Shang Culture from the perspective of stratigraphy, laying a foundation for the formation of Chinese archaeological stratigraphy.
4. Yinxu excavation site has become the cradle of cultivating Chinese archaeological talents. From here, the first generation of Chinese archaeological elites such as Li Ji, Dong Zuobin, Shi Zhangru, Gao Quxun, Liang Siyong, Guo Baojun, Yinda, Xia Nai and Hu Houxuan have emerged.
5. The excavation of Yin Ruins has responded positively to the prevailing suspicion of antiquity in Chinese academic circles since the early 20th century. With the existence of Shang Dynasty confirmed by archaeology, Chinese academia has been able to explore the "Xia Dynasty" in the relevant records.
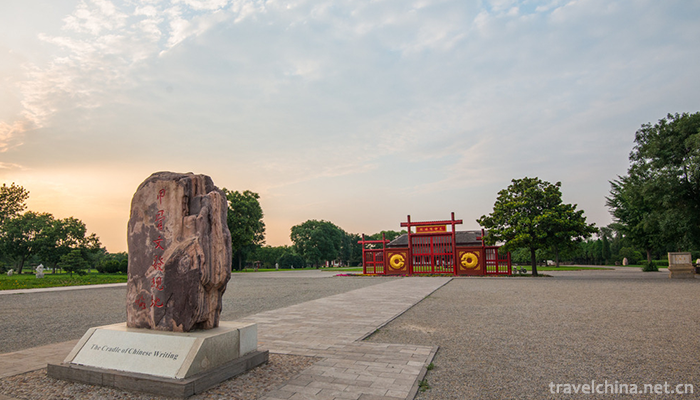
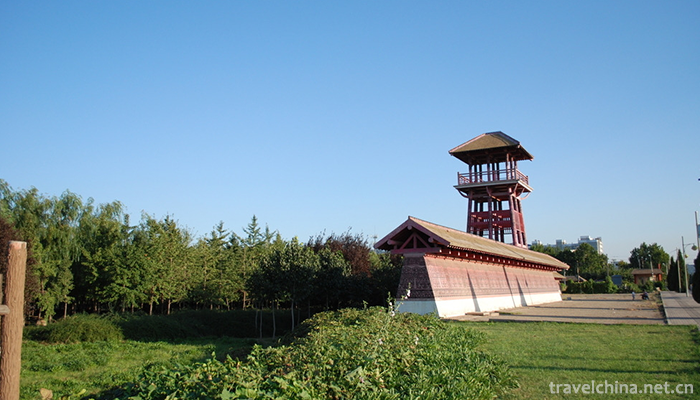
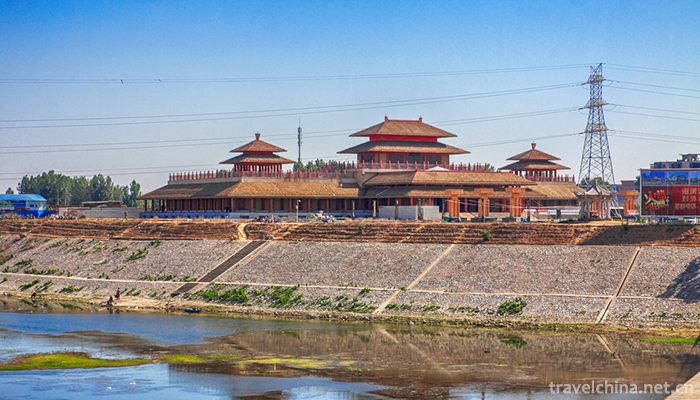








Yin Ruins Scenic Area (Yin xu)
-
Napa Lake
Naphai nature reserve is located in Shangri-La County, Diqing Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan
Views: 192 Time 2018-10-20 -
Xijiashan Folk House
Xijiashan Residence, a national key cultural relic protection unit and national AAAA-level tourist attraction, is located in Xijiashan Town, Jiang'an County, Yibin City, Sichuan Province
Views: 506 Time 2019-02-25 -
Drum bowl song
Drum-pot song is a very ancient traditional form of music and art in Hubei Province of China. It originates from the traditional folk activities of "beating a pot as a drum, singing with the fune
Views: 108 Time 2019-05-01 -
Nuuziz Festival
The word "Nuruzi" comes from the ancient Iranian language and means "spring rainy day". On March 21 of each year, like the Spring Equinox, it means the arrival of spring. Uygur, Ta
Views: 310 Time 2019-06-08 -
Making Techniques of Lianshi Paper in Lead Mountain
Lead Mountain Lianshi Paper Making Skills, local traditional handicraft in Jiangxi Province, one of the national intangible cultural heritage.
Views: 213 Time 2019-06-10 -
Cork paintings
Cork painting, also known as cork carving, woodcut. Chinese traditional folk sculpture crafts. It is mainly produced in Fuzhou, Fujian Province. It is a handicraft combining carving and painting. Simp
Views: 182 Time 2019-06-11 -
Chengdu University
Chengdu University, established in 1978 with the approval of the Ministry of Education, is a comprehensive University jointly built by Sichuan Province and Chengdu City. It is a key comprehensive univ
Views: 324 Time 2019-08-31 -
How long does it take for Chengdu to get to the giant panda base
When you come to Chengdu, you must come and see the lovely giant panda. The nearest panda base to the city is the giant panda breeding research base. How long does it take from Chengdu to the giant panda base?
Views: 74 Time 2020-12-13 -
Luzhou economy
In 2019, the GDP of Luzhou will reach 208.13 billion yuan, an increase of 8.0% over the previous year, 1.9 percentage points higher than the national average level (6.1%) and 0.5 percentage points higher than the provincial average level (7.5%). Among them, the added value
Views: 358 Time 2020-12-14 -
Administrative division of Guangyuan
Guangyuan City has 7 county-level administrative divisions (Municipal District 3, county 4) and 142 township level administrative divisions (Street 7, town 111, township 24). It covers an area of 16310 square kilometers and has a population of 3.11 million. Guangyuan Municipal People's government is located at No.24, north section of Renmin Road, Lizhou district.
Views: 114 Time 2020-12-15 -
Climate of Nanchong
Nanchong belongs to the subtropical humid monsoon climate. Compared with the Yangtze River Valley in the south of the basin, the temperature is relatively low, the rainy season is longer and the rainstorm is more. Compared with the Western Sichuan plain
Views: 284 Time 2020-12-17








