RenminbiChinese yuan
The legal currency of the People's Republic of China is Renminbi. The People's Bank of China is the competent organ of the state in charge of the management of Renminbi. It is responsible for the design, printing and issuance of Renminbi.
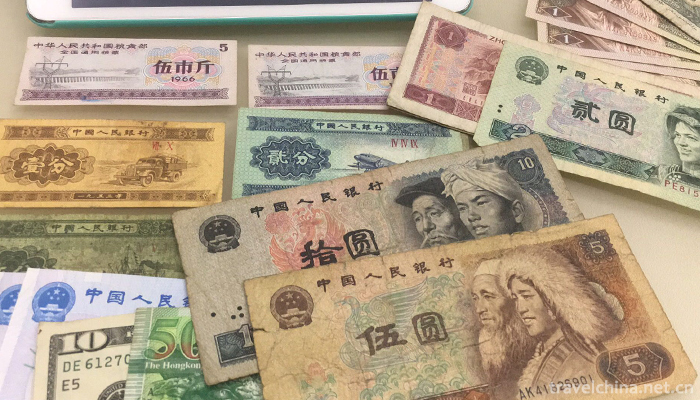
The unit of Renminbi is RMB, and the unit of Renminbi is RMB. 1 yuan equals 10 Jiao, 1 jiao equals 10 points. Since the issuance of RMB, the People's Republic of China has lasted more than 60 years. With the development of economic construction and the needs of people's lives, it has gradually improved and improved. Up to now, five sets of RMB have been issued, forming a multi-variety and multi-series monetary system, such as banknotes and metal coins, ordinary commemorative coins and precious metal commemorative coins. Apart from three kinds of coins, the first, second and third sets of RMB have been withdrawn from circulation. The fourth set of RMB will cease to circulate on May 1, 2018 (except for dime, fifty-cent notes and fifty-cent and one-dollar coins). The current circulation of RMB is mainly the fifth RMB issued in 1999.
On January 20, 2016, the People's Bank of China (PBC) revealed at a meeting held here that it would strive for the early introduction of digital currency issued by the central bank. The meeting held that under the new normal economic situation in China, it is of positive practical significance and far-reaching historical significance to explore the issue of digital currency by the central bank.
On November 30, 2015, the International Monetary Fund announced that the RMB would be formally included in the IMF SDR currency basket with a weight of 10.92%. The resolution came into force on October 1, 2016. Apart from the 1, 2 and 5 cent coins, the first set, the second set and the third set of RMB have withdrawn from circulation, and the fourth set of RMB has withdrawn from circulation since May 1, 2018. The fifth set of Renminbi is in circulation in the market; the banknotes in circulation are: 1, 50 cents, 1, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100 yuan; and the coins are 10 cents, 50 cents and 1 yuan.
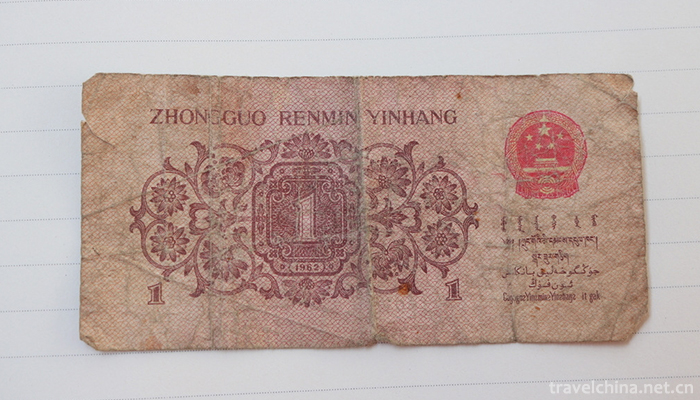
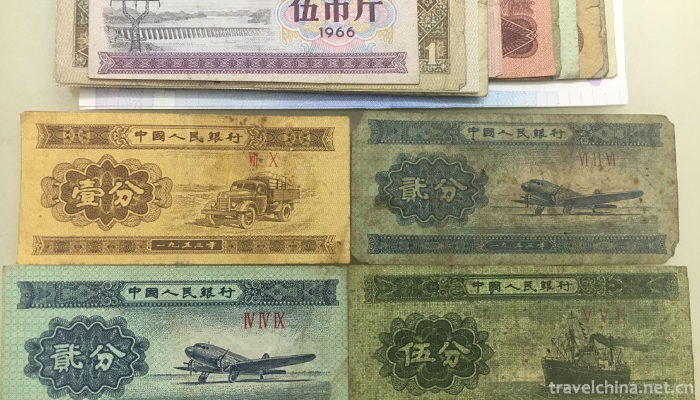
Among the five sets of Renminbi displayed in the China Coin Museum, the first set of Renminbi (except for the 1953 version of the Weihe Bridge pattern coupon of 5000 yuan) has six characters of the People's Bank of China and the denomination of Chinese characters arranged from right to left. When Chairman Mao reviewed the ticket edition in 1952, he proposed that the ranking of Renminbi names should be from right to left. Since 1953, the ranking of the People's Bank of China has changed from left to right.
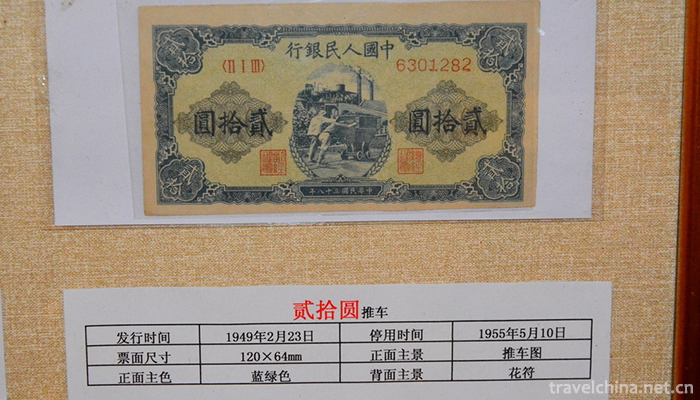
First set (December 1, 1948 to May 10, 1955)
The first set of renminbi was issued from December 1, 1948 to December 1953. There are 12 kinds of sixty-two kinds of denomination, including two kinds of 1 yuan vouchers, four kinds of 5 yuan vouchers, four kinds of 10 yuan vouchers, seven kinds of 20 yuan vouchers, seven kinds of 50 yuan vouchers, ten kinds of 100 yuan vouchers, five kinds of 200 yuan vouchers, six kinds of 500 yuan vouchers, six kinds of 1000 yuan vouchers, five kinds of 5000 yuan vouchers, four kinds of 10 000 yuan vouchers and two kinds of 50 yuan vouchers (1 yuan vouchers issued in 1949 for the positive Longevity Hill There are two different categories.
In 1948, along with the smooth progress of the People's Liberation War, the scattered liberated areas quickly joined together. In order to adapt to the development of the situation, a unified currency was urgently needed to replace the various liberated areas currencies which were complex and inconvenient to convert. To this end, on December 1, 1948, the People's Bank of China was established in Shijiazhuang City, Hebei Province. On the same day, a unified RMB was issued. Comrade Dong Biwu, then Chairman of the People's Government of North China, inscribed the bank name of the People's Bank of China for the set of RMB.
After the issuance of Renminbi, the circulation area was gradually expanded, and the local currencies in the former liberated areas ceased to issue and circulate one after another, and gradually recovered at the prescribed price. At the beginning of 1949, the head office of the People's Bank of China moved to Beiping (now Beijing). The branches of the People's Bank of China were established successively in various provinces, municipalities and autonomous regions. By the end of 1951, the RMB became the only legal currency in China and circulated throughout the country except Taiwan and Tibet (Tibet has officially circulated and used the people since July 15, 1957). Money).
On the day of its establishment, the People's Bank of China issued RMB 10, 20 and 50 yuan, all of which were printed in Nanyucun by the First Printing Bureau of the North China Bank.
The first set of Renminbi was not liberated nationwide when it was first issued. Therefore, the first set of early and medium-term edition of Renminbi still uses the chronology of "XX Year of the Republic of China", while the later editions only use the year of AD.
The unified issuance of Renminbi is an important measure to meet the national liberation. It clears away all kinds of currencies issued by the Kuomintang government, ends the decades of inflation under the rule of the Kuomintang and the history of the circulation and trading of foreign currencies, gold and silver coins in the market for nearly a hundred years, promotes the overall victory of the People's Liberation War and builds the country. The early economic recovery period played an important role.
Second sets (March 1, 1955 to April 1, 2007)
The second sets of Renminbi were issued in March 1, 1955 to April 20, 1962. On February 21, 1955, the State Council issued an order deciding that the People's Bank of China shall issue the second set of Renminbi and recover the first set of Renminbi from March 1, 1955. Because the influence left over by inflation for many years before liberation has not been completely eliminated, the first set of RMB has a larger value (up to 50,000 yuan) and a lower unit value. When calculating in circulation, the unit value is 10,000 yuan, which is not conducive to commodity circulation and economic development, and brings great inconvenience to people's lives. In addition, due to the limitations of material and technical conditions at that time, the paper quality of the first set of RMB is poor, there are many kinds of vouchers (62 kinds), the text description is single, and the par value is seriously damaged.
The second set of Renminbi and the first set of Renminbi conversion ratio are: the second set of Renminbi 1 yuan equals the first set of Renminbi 10,000 yuan. The second set of Renminbi issued on March 1, 1955 contains 10 kinds, including 1, 2, 5, 1, 2, 5, 5, 5, 1, 2, 3 and 5 yuan. On December 1, 1957, another set of Renminbi is issued for 10 yuan. At the same time, in order to facilitate circulation, the State Council issued an order to issue three kinds of coins, one, two and five cents, with the same value as paper cents, from December 1, 1957. Later, the designs and patterns of one-yuan notes and five-yuan notes were adjusted and changed. On March 25, 1961 and April 20, 1962, black one-yuan notes and brown five-yuan notes were issued respectively, which increased the number of the second set of RMB from 11 to 16, respectively. On April 14, 1964, the People's Bank of China issued the Notice on the Recovery of Three Kinds of RMB Vouchers. It decided to withdraw the 1953 edition of 3, 5 and 10 yuan banknotes printed by the Soviet Union within a time limit from April 15, 1964, and to stop the receipt and circulation on May 15, 1964. Since January 1, 1999, currencies other than cents have been stopped. Since April 1, 2007, three denomination notes, 1, 2 and 5 cents, have ceased to circulate, while three denomination coins are still in circulation.
The second set of RMB theme pattern embodies the style and features of socialist construction in New China, the fighting process of the Communist Party of China revolution and the theme of the great unity of the people of all nationalities. Banknote pattern breaks the original fixed four-sided frame form and adopts a new specification with symmetrical left and right patterns; the face size of the bill increases according to the size of the face; the whole pattern, lace and pattern lines are distinct, precise, beautiful and lively, with a national style. The second set of gravure plate of RMB is made by traditional Chinese hand-carving method. It has a unique national style. Its advantages are deep print, thick ink layer and good anti-counterfeiting function. Therefore, after the issuance of the second set of RMB, it was welcomed by the people and praised for its good looks, recognition, calculation and operation. Facts have proved that the second set of RMB has become China's first complete and exquisite currency, which has played an important role in improving China's monetary system and promoting socialist economic construction.
Third sets (April 20, 1962 to July 1, 2000)
The third sets of Renminbi were issued in April 20, 1962 to January 5, 1974. At that time, after three consecutive years of economic difficulties, under the guidance of the Party Central Committee's eight-character policy of "readjustment, consolidation, enrichment and improvement", China overcame many difficulties and vigorously developed production. With the approval of the State Council, the People's Bank of China began issuing the third set of Renminbi on April 20, 1962, in order to promote the development of industrial and agricultural production and the circulation of commodities and facilitate the use of the masses. Third sets of Renminbi and second sets of Renminbi denomination equivalents, and mixed circulation in the market.
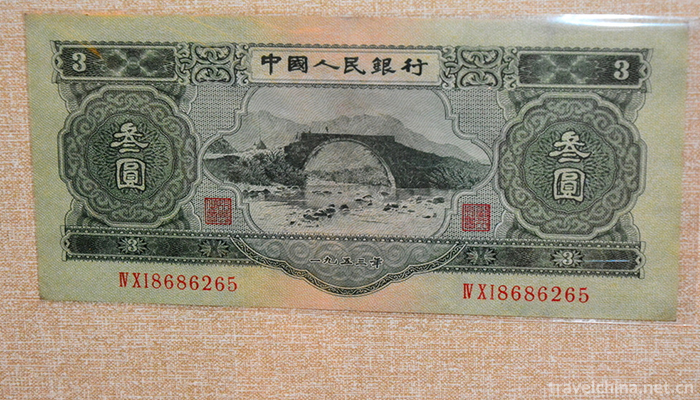
On the basis of the second set of RMB, the third set of RMB has been completely adjusted and replaced. The third set of RMB has cancelled the 3-yuan banknotes in the second set of RMB, and added four kinds of metal coins, namely, 1,2,5 and 1 yuan. From April 20, 1962, to April 15, 1980, the third set of RMB began issuing jujube red dime notes. After 18 years of gradual adjustment and replacement, 10 kinds of second set of RMB (except 6 kinds of paper and coins) were recovered and 13 kinds of third set of RMB were issued, of which 10 yuan paper was issued. Money, 5-yuan note, 2-yuan note, 1-yuan note, 5-cent note, 2-cent note, 1-dollar note, 3-dime note, 1-dollar coin, 5-dime coin, 2-dime coin, 1-dime coin.
The third set of RMB began to issue in April 20, 1962 and stopped circulation in July 1, 2000, which lasted for 38 years. This set of Renminbi has been unified since 1958. The par design pattern reflects the principle that the national economy of China was based on agriculture, dominated by industry and weighed by both workers and peasants. In terms of printing technology, the third set of Renminbi inherits and develops the technical tradition and style of the second set of Renminbi. In the process of plate-making, fine carving, combination of machine and traditional manual make the pattern and pattern lines fine; ink matching is reasonable, color is novel and bright; paper size is small, the pattern is beautiful and generous.
The third set of RMB coupons has reasonable structure, rich varieties of paper and coins, distinct design ideas and advanced printing technology. The issuance of the third set of RMB strengthens the anti-counterfeiting ability of RMB and plays an important role in improving China's monetary system and promoting economic development.
Fourth sets (April 27, 1987 to May 1, 2018)
The fourth sets of Renminbi were issued in April 27, 1987 to September 22, 1998. The fourth set of RMB is issued under the circumstances of economic development, increased retail sales of commodities and increased demand for money. With the implementation of the policy of reform and opening up at the Third Plenary Session of the Eleventh Central Committee of the CPC, China's national economy has developed rapidly and the retail sales of social goods have increased substantially. In order to meet the needs of economic development and further improve China's monetary system, on April 25, 1987, the State Council issued an order to issue the fourth set of RMB, ordering the People's Bank of China to issue the fourth set of RMB one after another from April 27, 1987.
Fourth sets of RMB 14 kinds of paper currency, adopt "one announcement, sub issue" method. On April 27, 1987, 50 yuan vouchers and 50 yuan vouchers were first issued. On May 10, 1988, 100 yuan, 2 yuan, 1 yuan and 20 yuan notes were issued. On September 22, 1988, 10 yuan, 5 yuan and 1 yuan notes were issued. In order to improve the anti-counterfeiting ability of RMB, the 1990 version of 50 yuan and 100 yuan banknotes were issued nationwide on August 20, 1992. According to Decree No. 97 of the State Council of 8 May 1992, the People's Bank of China has issued a fourth set of RMB 1 yuan, 50 cents and 10 cents since 1 June 1992. Fourth sets of RMB structure will be improved. In order to facilitate market circulation, the 1990 and 1996 editions of 1 yuan notes were issued nationwide on March 1, 1995 and April 1, 1997. In April 10, 1996, 2 yuan banknotes were issued in 1990.
The fourth sets of RMB have made some innovations and breakthroughs in design thinking, style and printing process. The 100-yuan bill uses side reliefs of Mao Zedong, Zhou Enlai, Liu Shaoqi and Zhu De, the older revolutionaries; the 50-Yuan bill uses the heads of workers, peasants and intellectuals; the other bills use the heads of 14 ethnic figures in China. In terms of design style, this set of Renminbi maintained and carried forward the characteristics of Chinese national art tradition. The backside of the coin is based on Chinese scenic spots, mountains and rivers. The backside decorations are all designed with Chinese national characteristics, such as Phoenix peony, crane pine, ribbon bird emerald bamboo, swallow peach blossom and so on. In the printing process, the main scenes all adopt large-scale personage head image watermarking, and the carving process is complex; the banknote paper adopts full-page watermarking and fixed portrait watermarking respectively, which not only shows the line picture, but also shows the level of light and shade. The technology is very high, which further improves the technical level of Chinese banknote printing technology and banknote anti-counterfeiting. Ability. At the same time, on the basis of the second and third sets of RMB, this set of RMB has increased the issuance of 50 yuan and 100 yuan coupons, which is of great significance for improving the efficiency of social work and giving full play to the role of RMB in the national economy.
Fourth sets of RMB notes (except 1 jiao, 5 jiao) and 1 jiao coins were suspended from circulation in May 1, 2018.
Fifth sets (October 1, 1999 to date)
The fifth set of Renminbi will be issued after September 28, 1999. Since the reform and opening up, with the sustained, healthy and rapid development of the socialist market economy, the demand for cash is also increasing. The design and printing of the fourth set of RMB is limited by the conditions at that time, and there are some shortcomings in itself, such as the simple anti-counterfeiting measures, which are not conducive to the anti-counterfeiting of RMB, the lack of machine-readable performance, and the disadvantage of automated processing of banknotes, etc. All these require timely issuance of new Renminbi.
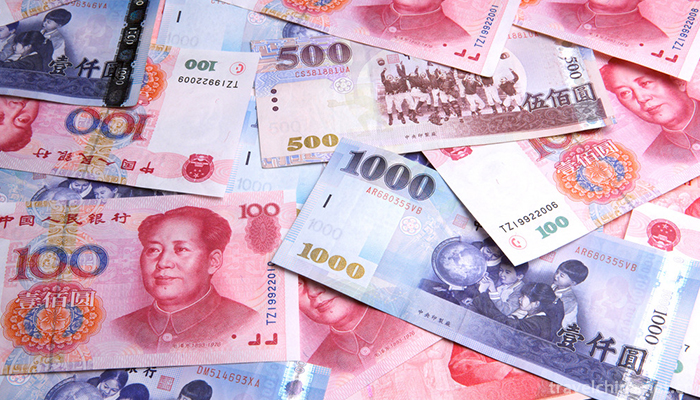
On October 1, 1999, on the occasion of the 50th anniversary of the founding of the People's Republic of China, the People's Bank of China issued the fifth set of RMB successively in accordance with Decree No. 268 of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. There are eight denominations in fifth sets of RMB: 100 yuan, 50 yuan, 20 yuan, 10 yuan, 5 yuan, 1 yuan, 5 jiao, 1 angle. The fifth set of Renminbi, based on the fact that the low denomination principal currencies in the market actually play a large role in finding change, has increased the denomination by 20 yuan and cancelled the denomination by 2 yuan, thus making the denomination structure more reasonable. The fifth set of Renminbi is to be "published once and issued separately". On October 1, 1999, 100 yuan notes were first issued; on October 16, 2000, 20 yuan notes, 1 yuan and 10 yuan notes were issued; on September 1, 2001, 50 yuan notes and 10 yuan notes were issued; on November 18, 2002, 5 yuan notes and 50 yuan coins were issued; and on July 30, 2004, 1 yuan notes were issued.
In order to improve the printing technology and anti-counterfeiting technology of the fifth set of Renminbi, the People's Bank of China issued the fifth set of Renminbi 2005 edition 100 yuan, 50 yuan, 20 yuan, 10 yuan, 5 yuan notes and stainless steel dime on August 31, 2005 with the approval of the State Council.
Since November 12, 2015, the 100 edition of the 2015 edition has been issued to enhance the anti-counterfeiting technical version.
The fifth set of RMB inherits the traditional experience of Chinese printing technology and draws lessons from the advanced technology of foreign banknote design. The improvement of raw material technology has improved the comprehensive quality and anti-counterfeiting of paper. Fixed watermark has strong three-dimensional sense and vivid image. Magnetic micro-text safety lines, color fibers and colorless fluorescent fibers are used in paper. Computer-aided design, manual engraving, electronic engraving and plate etching are combined in plate-making technology. Especially in the field of second and third-line anti-counterfeiting, international common anti-counterfeiting measures are adopted, which provide conditions for professionals and researchers to identify authenticity. Compared with the fourth set of Renminbi, the fifth set of anti-counterfeiting skills of Renminbi has increased from more than a dozen to more than twenty. The main scene portraits, watermarking and denomination figures are all enlarged compared with the previous ones, which is convenient for people to identify. The fifth set of RMB has applied advanced science and technology, and has greatly improved its anti-counterfeiting performance and adapted to the modernization of currency processing.
The fifth set of Renminbi faces adopt Comrade Mao Zedong's head in the early days of the founding of the People's Republic. The background uses the famous flower pattern of China. On the back, the main landscape patterns are the Great Hall of the People, the Potala Palace, Guilin Landscape, the Three Gorges of the Yangtze River, Mount Taishan and the West Lake of Hangzhou.












-
1.Red Cooked Chicken Daokou Style
Red-Cooked Chicken, Daokou Style is one of the traditional specialties. It is made by Yixing Zhang family roast chicken shop in Daokou Town, Huaxian County, Henan Province
Time 2018-11-26 -
2.Nanshan Cultural Tourism Zone
Nanshan Cultural Tourist Area is located 40 kilometers southwest of Sanya City, Hainan Province. It is the southernmost mountain in China. It belongs to tropical marine monsoon climate.
Time 2018-12-12 -
3.Guanmenshan National Forest Park
Guanmenshan National Forest Park is located 70 kilometers southeast of Benxi City. The Forest Park covers an area of 3517 hectares, with an altitude of 310-1234 meters and a forest coverage
Time 2018-12-24 -
4.Thrush valley ecological tourist area
Thrushcross Valley is a natural eco-tourism area, located in Yaoshan Town, Lushan County, Henan Province, and at the northern foot of Yaoshan Scenic Area. It is a national AAAA-level tourist attractio
Time 2019-01-17 -
5.qingdao olympic sailing center
Qingdao Olympic Sailing Center Scenic Spot is located in Fushan Bay, Qingdao City, and Qingdao's landmark scenic spot - May 4th Square offshore, covering an area of about 45 hectares
Time 2019-02-07 -
6.Tianjin Polar Ocean World
Tianjin Polar Ocean World is a theme park invested by Dalian Haichang Group in Tianjin. Tianjin Polar Ocean World is a large-scale open tourism project with the theme of Ocean Park
Time 2019-02-21 -
7.Beipiao Folk Stories
Beipiao Folklore is a local folk literature in Liaoning Province. It includes eight categories: folklore, character legend, fantasy story, life story, animal and plant story
Time 2019-04-04 -
8.Huian stone carving
Hui'an stone sculpture mainly served religion in its early stage, with strong religious color. It is mainly embodied in the architectural design, sculpture and installation of the temple,
Time 2019-05-05 -
9.Story telling in Beijing dialect with drum accompaniment
Jingyun Dagu is one of the Chinese folk songs. Developed from the popular wooden drum in Cangzhou and Hejian of Hebei Province, it was formed in Beijing and Tianjin. After the introduction of Hebei wo
Time 2019-05-07 -
10.Forging Skill of Longquan Sword
Longquan sword forging technology, the traditional arts and crafts of Longquan County, Zhejiang Province, is one of the national intangible cultural heritage.
Time 2019-05-14 -
11.Manchu embroidery
Manchu embroidery, commonly known as "needle embroidery", "tie flowers" and "embroidery", was originally popular in the vast rural areas where Manchu people lived togethe
Time 2019-05-16 -
12.Weaving and Dyeing Techniques of Uygur Felts and Printed Fabrics
Uygur felt, printing and dyeing technology, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Turpan (now Turpan) local traditional skills, one of the national intangible cultural heritage.
Time 2019-06-26