Traditional Building Techniques of Beijing Siheyuan
Traditional Building Techniques of Beijing Siheyuan
Beijing quadrangle traditional craftsmanship, Beijing local traditional handicraft, one of the national intangible cultural heritage.
Beijing courtyard is a traditional layout form of residential buildings in northern China, and also reflects the etiquette specifications of "front hall and back bed" in China. Siheyuan has a long history. It was gradually formed in the Han Dynasty, widely used in the Tang and Song Dynasties, and completed in the Ming Dynasty. A large number of quadrangles built in the Qing Dynasty now exist in Beijing.
On May 23, 2011, the traditional construction techniques of Beijing Siheyuan were approved by the State Council and listed in the third batch of national intangible cultural heritage list, heritage number: _-208.
historical origin
Since the capital of Beijing was built in the Yuan Dynasty (1276), large-scale planning and construction of the capital (1276), quadrangles and palaces, government offices, neighborhoods, lanes and alleys in Beijing have appeared simultaneously. At that time, Kublai Khan, the ancestor of the Yuan Dynasty, ordered eight acres of land as a part of his residence to build residences for the officials who moved to Beijing. From then on, the traditional courtyard houses in Beijing began to take shape on a large scale.
After the Ming Dynasty seized the Yuan metropolis and moved the capital from Nanjing to Beijing, the capital of the Ming Dynasty did not abandon the old city of the Yuan metropolis, but restored the city walls of the Yuan metropolis and developed the capital of the Ming Dynasty on this basis. At that time, in order to reduce the amount of projects and shorten the line of defense, the area of Wuhuali in the north of the Yuan metropolis was marked out outside Mingcheng, and tens of thousands of wealthy households were moved from Zhejiang, Shanxi and other places, which greatly promoted the development of Beijing's economy and the change of its urban outlook at that time. The residential areas in Ming Dynasty were basically similar to those in Yuan Dynasty, and the roads developed on the basis of Yuan Dynasty. Hutong is divided into rectangular residential areas with a distance of about 70 meters, and quadrangles are built side by side in the middle. The courtyard is regular and continuous, covering the whole area. At that time, the urban space did not emphasize public life, and there were few public spaces and concentrated green space in the whole neighborhood. Therefore, people in residential neighborhoods paid more attention to the construction of their own houses and planted all kinds of flowers and trees in the houses.
After the capital of Beijing was built in the Qing Dynasty, the whole urban pattern did not change, and basically followed the architectural style of the Ming Dynasty. But because of the destruction of natural forces such as fires or earthquakes, many buildings were renovated at that time. In the early Qing Dynasty, the system of flag people living in separate cities was implemented, so that all the Han people in the city moved to the outer city. The inner city was only full of people to live in, and many princes and nobles'residences were built. This measure also objectively promoted the development of the outer city.
During the Ming and Qing Dynasties, the quadrangles in Beijing City accounted for about half of the residential buildings, and had developed into the peak period of quadrangles. The courtyard of Ming and Qing Dynasty inherited the style of Yuan Dynasty courtyard well, and developed and perfected constantly under the new situation, showing some differences from Yuan Dynasty courtyard: for example, the courtyard of Ming and Qing Dynasty canceled the I-shaped plane of Yuan Dynasty courtyard, changed to a quadrangle plane composed of main room, East and west chamber room and handwriting corridor; the courtyard of Ming and Qing reduced the area of the front courtyard and expanded it. The area of the backyard makes the space center in the backyard, which is also the most central living area of the courtyard, making the space layout more reasonable. In addition, the area of the house foundation of the courtyard is generally reduced.
At the end of the Qing Dynasty, foreign invaders invaded and China became a semi-feudal and semi-colonial society. Traditional culture has been impacted by Western culture, and Beijing courtyard buildings have also been affected. Some Chinese and Western courtyard buildings have appeared. On the basis of the traditional courtyard, we add the decorative elements of Western architecture, such as the "Yuanmingyuan" courtyard gate in a specific period.
After the founding of New China, in order to meet the needs of new urban development, the use nature of many Beijing courtyards has changed, and some courtyards have become public houses. Changes in the nature of use have led to the transformation of many courtyards because of functional needs. Even the courtyard, which is still a private residence, has undergone great changes in the rapid development of the city today, and has revealed many practical problems. With the rapid increase of migrant population in Beijing, a large number of quadrangles have been rented out. The original single-family quadrangles have gradually become "big and miscellaneous courtyards". The living conditions are bad, and the sense of quiet and comfort of the original quadrangles has been completely lost. After the catastrophe of the "Cultural Revolution", the courtyard space is beyond recognition.
Process characteristics
Culture
The construction of Beijing courtyard contains rich cultural ideas. The depth, opening and closing of the courtyard, as well as the details of the gate, the wall and the house decoration, all clearly reflect the hierarchical color of the ancient dwellings. Family members and servants live in the main room, ear room, compartment and inverted room respectively. The difference of status and rank is reflected by the location, orientation, width and height of the buildings. The houses in each direction are connected as a unified whole, and the superiority and inferiority are orderly. It reflects the ethical connotation of traditional social family organization and has important sociological significance. The grey walls and grey tiles of Beijing courtyard constitute the basic urban color of Beijing and form the unique residential culture of Beijing.
type
Beijing courtyard is limited by geographical environment because of the difference of scale and grade, and forms various types. Common types are as follows: first, second, third, fourth and compound courtyards. Among them, the first courtyard is a basic quadrangle, which belongs to small courtyard; the second and third courtyards, which belong to medium courtyard; the fourth and compound courtyards, which belong to large quadrangle courtyard. Three into the courtyard, for the standard quadrangle.
pattern
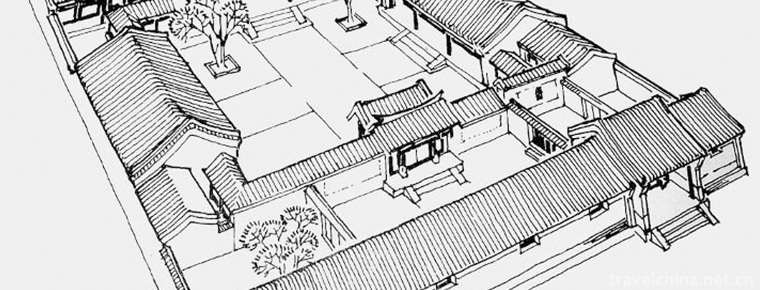
Four-in-one, four-in-one refers to the east, west, South and North sides. Four-in-one refers to the building surrounded by four sides, forming a "mouth" structure. After hundreds of years of construction, Beijing Siheyuan has formed its unique Beijing style from plane layout to internal structure and detailed decoration.
Beijing's regular courtyards are generally sitting in the East-West alleys facing the north and the south. The basic form of the courtyards is divided into the North (main room), the South (inverted room) and the East and West chambers. The courtyards are surrounded by high walls to form a four-way closure and open a door. The gate is located in the southeast corner of the house. The total number of rooms is generally 3 in the north, 2 in the ears and 5 in the east, 3 in the west, 4 in the south, 17 in the gate hole and flower gate. If calculated at 11-12_per room, the total area is about 200_.
The courtyard is surrounded by four houses: the main house (north house), the reversed house (south seat), the east room and the West room, forming a "mouth" shape, which is a central courtyard, so this courtyard-style dwelling is called the courtyard.
details
Detailed design of the courtyard purlin, columns, beams, sills, rafters, doors, windows, partitions, etc. are all made of wood, while brick walls are used around wooden house shelves. Beams and columns, doors and windows, and eaves and rafters are painted. Although they are not as brilliant as palace courts, they are also colourful. Wall is used to grinding bricks, broken bricks and masonry, so-called "Beijing City has three treasures..." Bad bricks and walls will not fall down. The roof tiles are mostly made of green slab tiles, which are interlocking, dripping in front of the eaves, or not tiled. They are all covered with green plaster, called "grey shed".
Technological process
- Wall masonry
The main walls of the courtyard are the front eaves and sills, the gables, the back eaves and the legs. The gables, the back eaves and the legs are divided into the upper wall and the lower alkali. The lower alkali or sill walls are mostly dry-laid (pavilion mud), and the upper part is made of silk joints (pavilion mud); the lining walls are made of more materials, including aerated concrete bricks. Shale brick, lime sand brick, concrete hollow block and so on. The external appearance of the wall generally adopts the traditional technology and materials of ancient construction, basically maintaining the traditional practice.
The wall thickness of the courtyard is usually about 500 mm. The wall thickness of the courtyard is the thickest, which can reach 600-700 mm. The wall of the courtyard is usually composed of two parts. The outer dry pendulum or silk joints are built with traditional materials of ancient buildings. The inner back wall is built with gymnastic bricks. The back wall and the dry pendulum or silk joints wall should be left with grouting openings of about 20 mm to pour cement. Exterior decorative wall and back-interior wall require reliable connection, which is usually met by tied bars. Insulation material can be placed in the middle of the wall, usually EPS or XPS board.
- Thermal insulation structure
The thermal insulation material is usually set between the ancient building wall and the lining wall. The thermal insulation board and the back wall can be bonded by polymer mortar or fixed nail method, and the back wall can be fixed by S-shaped pull-in steel bar, and the pull-in steel bar is @500-600 mm. The outer side of the thermal insulation board is provided with a steel mesh of 4-6 mm @400-600 mm, and the outer ancient building can be connected by S-shaped steel bar @500-600 mm. Traditional material - Pavilion mud brick (pavilion mud brick, Pavilion mud brick), the inner surface of the brick body is cut into grooves, the remaining five sides are grinded according to traditional technology (commonly known as "five skins"), the steel bar is pulled into the upper and lower cracks of the brick, and then poured 1:1 cement slurry according to @500-600 mm, so as to ensure that the cement slurry filling is full, the construction of the grouting should pay attention to ensuring the integrity of the external wall. Pollute the walls.
Roofing works
In Beijing, the roof structures of courtyard buildings are mainly wood base and reinforced concrete roof.
Wood base roof
After the wooden Watchboard is laid out, the gaps of the Watchboard are wiped with a hemp knife grey hook. If the gaps are too large, it needs to be filled with wooden strips, and then the protective board grey is made. The back layer of traditional roof mainly includes: protective slab ash, roof mud back and green ash back. The Watchboard is sewn with hemp knife ash. The guard board ash is usually hemp knife ash. The average thickness is 15-20 mm. After 70% of the Watchboard is dried, the next process can be continued. The back of mud is usually mixed with mortar, the ratio is loess: white ash = 5:5, the average thickness is 50-100mm, and it is completed and compacted twice. About 78% of the mud back is dry, and the average thickness of the mud back is 30 mm. The proportion of the mud back is white ash: green ash: hemp knife = 100:8:3. The hemp knife should be made of high quality materials, compacted by calendering, and the surface is free of cracks. Finally, it is very important to mix mortar into the construction quality of lime back.
Reinforced concrete roof
In order to reduce the roof load, most roofing practices cancel the mud back and lime back, and correspondingly increase the roof waterproof layer and thermal insulation layer. This is to ensure the waterproof effect of the roof, but also to improve the traditional roofing practices and technology.
Roof laying
The tile surface of quadrangle courtyard generally has composite tile roof and tubular tile roof. The roof of composite tile roof is in the form of clear water ridge. The tubular tile roof mostly adopts the form of dragon ridge. Although the roof engineering has made some improvements in the method of the back layer of the roof, the roof should still follow the traditional construction technology, and adopt the method of mixing mortar (tile or tubular tile). The overall appearance of the tile surface is still the traditional style of ancient buildings. Sample. When the roof slope is steep and the length is more than 5 m, in order to prevent the roof tile from sliding, certain anti-skid measures must be taken. Usually, steel mesh is installed on the roof to fasten the tile and steel mesh with copper wire.
Taiming masonry
Stairs and steps of single courtyard buildings are usually made of blue-white stone, including stepping stone, steep slate, buried stone, vertical belt, step step, inkstone and other stone activities.
The inner wall of the back of the platform and the steep board is usually built directly by the foundation wall, but when the foundation wall is built to the elevation of the outdoor surface, the size of the steep board and the size of the material used for the steep board should be considered to leave the position of the surface layer. At this time, the foundation wall plays the role of the inner wall of the back of the ancient building wall, so the installation size of the stone material should be considered when building the foundation wall. In addition, the position of buried stone should be reserved at the corner of Taiming. According to the thickness of buried head in the design drawings, the conventional size of buried head is 130-150 mm. The upper stepped stone and marble are pressed on it, which is 5-8 mm wider than buried stone. The installation of stone materials and the filling of 1:1 cement slurry are often used between the masonry wall and the masonry wall to ensure the firmness of the connection between the stone and the wall.
- Door and window works
The traditional quadrangles are mostly wooden doors and windows. The doors and windows of the quadrangles are mostly in the form of supporting and removing windows. The upper side is supporting and removing windows, and the lower part is fixed windows. Most of the doors are four separate doors or four single doors. The windows and doors are 3 mm in size. The supporting and removing windows are made of one glass and one yarn. The fixed part is a single-layer glass window. Yarn fans are generally in the form of traditional lattices built in ancient times, and doors between Ming Dynasty and Ming Dynasty are generally in the form of partition doors.
Inheritance and protection
Inheritance value
Although Beijing Siheyuan is a residential building, it contains profound cultural connotation and is the carrier of Chinese traditional culture.
First of all, the construction of Beijing quadrangle is very particular about geomantic omen. From the choice of location and location to the determination of the specific scale of each building, it must be carried out according to geomantic omen theory. The geomantic omen theory, in fact, is the architectural environment of ancient China. It is an important part of the traditional architectural theory of China. It has been guiding the construction activities of ancient China for thousands of years.
Secondly, the decoration, sculpture and paintings of Beijing Siheyuan embody folk customs and traditional culture everywhere, and show people's pursuit of happiness, beauty, wealth and auspiciousness under certain historical conditions. For example, the sculpture pattern consisting of bats and longevity characters implies "both happiness and longevity"; the pattern of roses placed in vases implies "peace of the four seasons"; and the auspicious words embedded in doorways and doorways, the couplets with pillars attached to the eaves, and the excellent paintings and calligraphy hanging in the interior, collect ancient and philosophical precepts, adopt ancient and modern famous phrases, or eulogize the beauty of mountains and rivers, or inscribe the study of life, or Yong Honggu's ambition, elegant, full of rich cultural atmosphere, Dence Courtyard, like entering a palace of traditional Chinese culture.
Thirdly, Beijing courtyard has rich cultural connotations, which fully reflects the traditional Chinese concept of living. Taking the small courtyard as an example, this kind of courtyard is very suitable for families with two or three generations. Usually, the elders live in the main room, the younger in the box room, and the south room serves as the living room and study. In the courtyard, the houses on all sides open doors to the middle of the courtyard. The family is friendly and beautiful in the courtyard.
Finally, Beijing courtyard can exist for hundreds of years in history because it has the advantages that other residential buildings are difficult to compare.
Inheritance status
With the rapid development of Beijing's urban construction, Beijing courtyard has been greatly damaged, and its construction skills are gradually losing due to the impact of modern architectural methods. It is urgent to protect the traditional construction skills of Beijing courtyard.
Many practices of traditional architecture have been lost, although many traditional building types of construction technology and crafts are still used everywhere, but most of them are passed down through the way of words and deeds between teachers and apprentices, so the inheritance and development of traditional construction techniques of Beijing Siheyuan has a long way to go.
protective measures
In the 1980s, Beijing clearly put forward the overall protection of Beijing's old city and the protection of historical and cultural areas. For the first time, the concept of patchwork protection was put forward for the residents of quadrangles.
In 1982, in Beijing's urban master plan, 1-8 districts in the West and four north of Xicheng and Luogu Lane in the south of Dongcheng were included in the Siheyuan Reserve Area.
In 1990, urban planning proposed to divide 25 historical and cultural reserves in the old urban areas. In 2000, the planning concept of 25 protected areas was submitted to the municipal government, which approved the implementation in 2002. In 2004, the urban planning increased the number of historical and cultural protected areas in the old city from 25 to 33, and was approved by the municipal government for implementation.
In 1993, the State Council's approval of the Beijing Urban Master Plan (1991-2010) established the concept of "overall protection", and established an overall protection system for intangible cultures, such as single historical buildings, temples, scenic spots, urban patterns, commercial districts, blocks, alleys, traditional quadrangles, residential areas and traditional living areas, as well as the most Beijing-flavored culture and local customs.
social influence
In 2016, Beijing Siheyuan Chronicle, compiled by Beijing Local Chronicle Compilation Committee Office for five years, was recently published by Beijing Publishing Group. The book systematically combs the origin, shape and cultural concept of Beijing quadrangle, and records the protection, utilization and evolution of Beijing quadrangle, among which 923 courtyards are well preserved, reflecting the unique folk culture of Beijing.


-
Nanjiang Grand Canyon
Nanjiang Grand Canyon is located in Kaiyang County in the middle of Guizhou Plateau, 54 kilometers away from Guiyang, the capital of Guizhou Province.
Views: 113 Time 2018-12-31 -
Jiangshan Peninsula Tourist Resort
Jiangshan Peninsula Tourist Resort is a provincial tourism resort development zone approved by the People's Government of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region in 1994..
Views: 166 Time 2019-01-21 -
kangbaiwan manor
Kang Million Manor, also known as Heluo Kangjia, is located in Kangdian Town, Gongyi City, Henan Province (formerly Gongxian County). It was built in the late Ming and early Qing Dynasties.
Views: 192 Time 2019-01-29 -
Senbora Resort Forest Scenic Area
Senbora, a landscape world in ancient forests, a paradise of pleasure water under glacial ruins, a national 4A-class tourist attraction, is located at the exit of Fogang Expressway in Fogang County.
Views: 187 Time 2019-02-07 -
Swan Lake National Urban Wetland Park
Swan Lake National Urban Wetland Park, located in the ecological zone between the East and West urban areas of Sanmenxia City, covers an area of 8 850 mu, including 6 150 mu of land.
Views: 179 Time 2019-02-21 -
Zizhuyuan Park
Zizhuyuan Park is located in the West Third Ring of Beijing, near Baishiqiao in Haidian District, west of Beijing Capital Stadium. Zizhuyuan Park was built in 1953. It was named for the Ming and Qing .
Views: 263 Time 2019-03-22 -
Stories of Marine Animals
Marine animal stories are mainly handed down orally. The traditional folklore stories circulated in the islands for a long time have been formed and disseminated in Dongtou.
Views: 274 Time 2019-05-02 -
Huidong Fishing Song
Huidong Fishing Song is one of the traditional folk arts in Guangdong Province. From the Song Dynasty, fishing songs in the shallow sea of Huidong were introduced from the coast of Fujian Province..
Views: 178 Time 2019-05-05 -
Xiamen lacquer line carving skills
Xiamen lacquer line carving technique is to use old brick powder, large paint and cooked tung oil as raw materials to mix, repeatedly beat into soft and resilient clay (commonly known as "lacquer.
Views: 84 Time 2019-06-12 -
Ring Dance of Yi Nationality
Ling Dance of the Yi Nationality, to be known as foot-jumping, is called "Qi He Zhe" in the Yi language, which means the spiritual farewell dance. It is a traditional folk dance performed an.
Views: 125 Time 2019-07-12 -
Recitative
Recitation is a local traditional music form in Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province, which has a high reputation at home and abroad. The art of reciting belongs to "minority culture", which is .
Views: 91 Time 2019-07-13 -
Neijiang administrative division
Neijiang City governs 5 county-level administrative divisions (Municipal District 2, county-level city 1, county-2), and 83 township level administrative divisions (street 13, town 70). It covers an area of 5386 square kilometers and has a population of 4.27 million..
Views: 158 Time 2020-12-16











